Discover how specific diets, from fasting to Mediterranean, can repair cells, reduce inflammation, and regulate metabolism – key factors in promoting health and preventing related diseases old age.
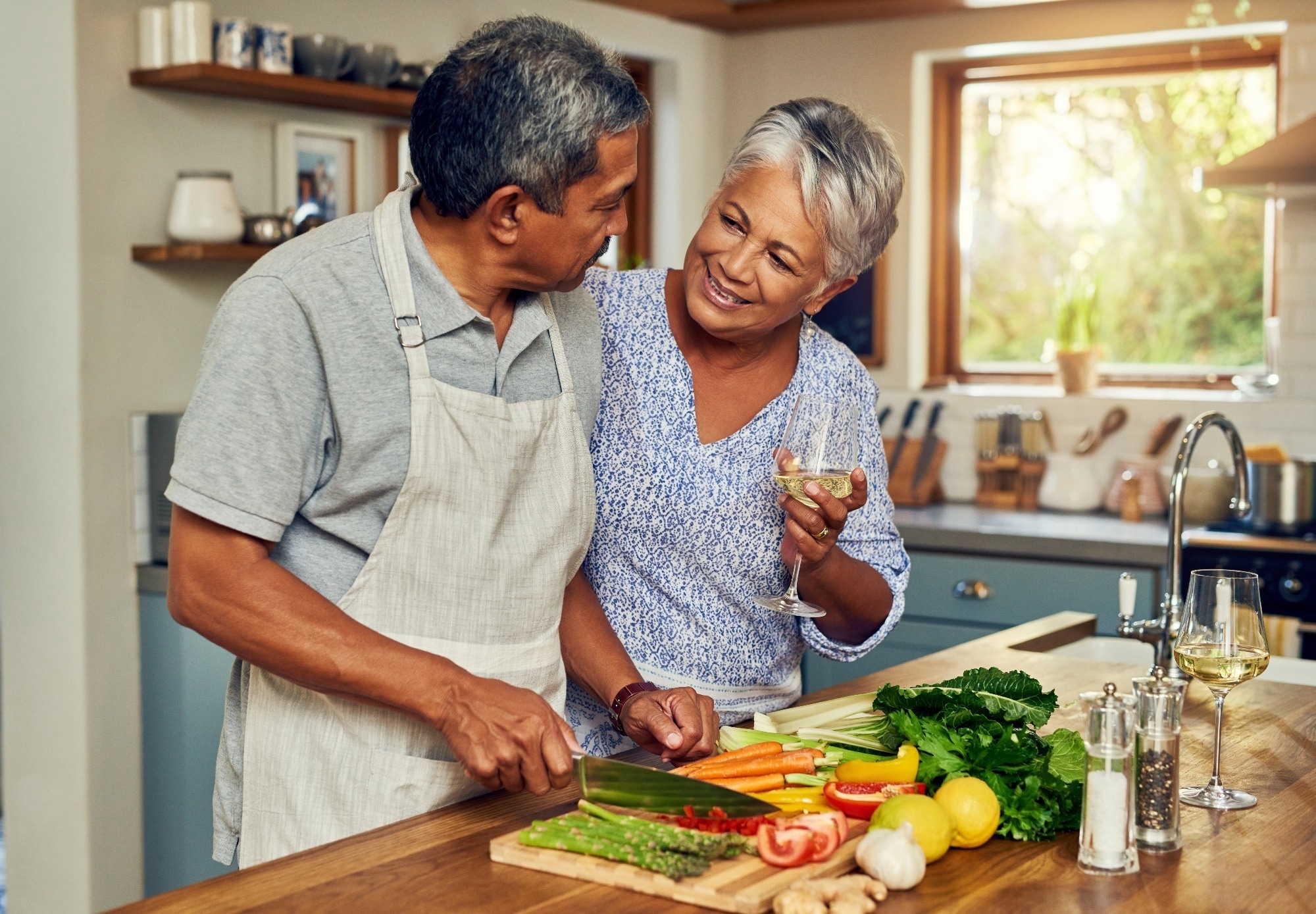 Education: Molecular Mechanisms of Healthy Aging: The Role of Calorie Restriction, Intermittent Fasting, the Mediterranean Diet, and the Ketogenic Diet-A Scoping Review. Image credit: PeopleImages.com – Yuri A / Shutterstock.com
Education: Molecular Mechanisms of Healthy Aging: The Role of Calorie Restriction, Intermittent Fasting, the Mediterranean Diet, and the Ketogenic Diet-A Scoping Review. Image credit: PeopleImages.com – Yuri A / Shutterstock.com
In a recent study published in the journal Energyresearchers explored how certain dietary patterns can promote healthy aging by influencing key molecular pathways.
Problems of the elderly
Rising life expectancy figures have increased the world’s population from three billion in 1950 to eight billion in 2022. Despite the increase in life expectancy, saving time the right of health, defined as the period of good health, is still a challenge in society.
Chronological age (CA) is often used to assess aging; however, due to individual differences, it may not accurately reflect biological aging. This has led researchers to look for other biological markers that can measure aging more accurately.
Nutritional interventions have emerged as a promising strategy to overcome aging-related problems and improve health outcomes. Thus, it is important to examine how diet affects the molecular pathway associated with aging and to develop individualized strategies for healthy aging.
Calorie restriction and intermittent fasting
Calorie restriction involves reducing calorie intake while ensuring adequate nutrition. Recent studies suggest that it improves metabolic health, reduces the risk of obesity, and slows the development of age-related conditions, such as brain tumors and muscle loss.
For example, one study of 218 non-obese people between the ages of 21 and 51 reported that a 25% reduction in calories led to weight loss, improved lipid levels and a slower rate of aging compared to those on a normal diet. . However, the long-term effects of CR on health and aging remain unclear.
Intermittent fasting involves alternating periods of fasting and regular meals. In some species, such as worms and fruit flies, short-term fasting measures can increase lifespan. Additionally, another study with 60 participants between the ages of 48 and 52 who did alternate-day fasting (ADF) for four weeks showed improvements in physical fitness, cardiovascular health and risk reduced risk of future heart attacks.
Long-term fasting has been shown to reduce inflammation and improve cholesterol levels. In fact, one study with 24 adults who practiced long-term fasting (TRF) for six weeks showed a decrease in heart rate and hunger; however, no significant impact on heart function or other health indicators was observed.
Mediterranean food
The Mediterranean diet, which is rich in vegetables, fruits and olive oil and low in saturated fat, is well documented for preventing the development of age-related conditions. This diet emphasizes the balanced use of essential nutrients and antioxidants, which promote healthy aging.
In another live study, rats fed extra virgin olive oil showed lower levels of harmful proteins and better expression of genes related to mitochondrial function and oxidative stress.
Another study on 1,279 people between the ages of 65 and 79 found that the Mediterranean diet slows down biological aging and improves cognitive function, especially in women. In addition, a recent study showed that this diet changed the symptoms of intestinal microbiota and led to a reduction in the expression of inflammatory markers.
The ketogenic diet
A ketogenic diet, characterized by a high-fat and low-carbohydrate diet, has been shown to prolong life and improve cognitive function in certain animal species. However, clinical trials in humans have focused mainly on the effects of this dietary intervention to promote weight loss, with mixed results regarding its effects on heart health.
For example, one study comparing a ketogenic diet with a Mediterranean diet in people with diabetes or type 2 diabetes found that, although both diets led to weight loss, the diet ketogenic diets were associated with higher levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol. it is considered dangerous.
One trial reported that a ketogenic diet can lower cholesterol levels; however, this diet also led to decreased appetite and stomach problems, thus raising concerns about its suitability for the elderly. Overall, more research is needed to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the ketogenic diet in this patient population.
Decisions
Notable strengths of the current study include its comprehensive analysis of different dietary patterns and their effects. However, other limitations associated with this include heterogeneity in study designs, limited time, and lack of systematic review.
Future research should focus on chrononutrition, which shows how the timing of meals affects metabolic processes and health, the effect of specific diets on aging, and screening tools to measure the relationship between diet and health. beauty. These data will support the development of nutritional strategies to improve health and reduce age-related conditions.
Journal reference:
- Surugiu, R., Iancu, MA, Vintilescu, Ș. B., and al. (2024). Molecular Mechanisms of Healthy Aging: The Role of Calorie Restriction, Intermittent Fasting, the Mediterranean Diet, and the Ketogenic Diet-A Scoping Review. Energy. doi:10.3390/nu16172878